
Population
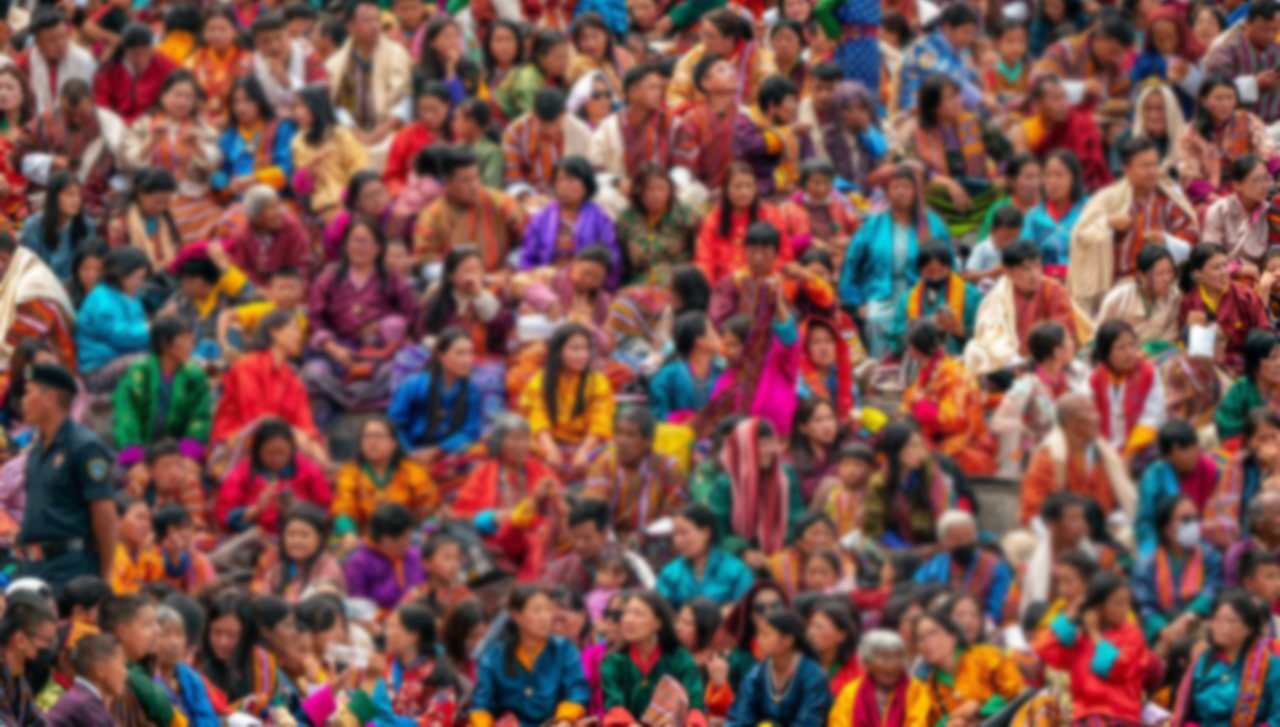

As of 2022, Bhutan’s population was estimated to be around 770,000 people. Bhutan is a relatively small country located in the eastern Himalayas, bordered by India to the south, east, and west, and by China (Tibet Autonomous Region) to the north. Understanding Bhutan’s population dynamics helps in appreciating its cultural diversity, economic development challenges, and efforts towards sustainable development and social cohesion. For the most current population figures and demographic trends, checking recent data from sources like the Royal Government of Bhutan or international organizations would be advisable.
Key points about Bhutan’s population:
- Population Growth: Bhutan has experienced moderate population growth over the years, with efforts to manage growth through policies that balance economic development with environmental and cultural preservation.
- Ethnic Diversity: Bhutan is ethnically diverse, with the largest ethnic group being the Ngalops (people of western Bhutan), followed by the Sharchops (people of eastern Bhutan) and the Lhotshampas (people of Nepalese origin residing mainly in southern Bhutan).
- Urbanization: Urbanization is increasing in Bhutan, particularly in major towns such as Thimphu (the capital), Paro, Punakha, and Phuentsholing. Urban areas offer employment opportunities in government,Health, tourism, education, and pvt. Sectors.
- Rural Population: Despite urbanization, a significant portion of Bhutan’s population still resides in rural areas, engaged in agriculture, livestock farming, and traditional crafts.
- Demographic Challenges: Bhutan faces challenges related to population distribution, access to healthcare and education in remote areas, and maintaining cultural traditions amid modernization.
- Youth Population: Like many countries, Bhutan has a youthful population, with a significant percentage under the age of 25. This demographic trend influences policies related to education, employment, and social development.
- Healthcare and Education: Bhutan has made strides in improving healthcare and education services, with efforts to provide universal access to basic services and promote well-being under the Gross National Happiness (GNH) framework.
Related
- Accomodation
- Bhutan Tourism Policy
- Businesses
- Currency
- Drink & Beverage
- Education
- Festivals
- Food & Restaurant
- GNH – Gross National Happiness
- Health Care
- How to get to Bhutan
- Language
- Media
- Night life
- Politics
- Population
- Religion
- Telecommunication
- Tour Booking info
- Transportation
- Weather
Need Assistance?
Need Help? Call us or drop a message. Our agents will be in touch shortly.
Call Us : +975-17351324
+975-17495729
Email Us : adbhutantours@gmail.com
Call Us : +975-17351324
+975-17495729
Email Us : adbhutantours@gmail.com
Send your Queries
